Animation depicts high elevations in red and lower elevations in blue and green
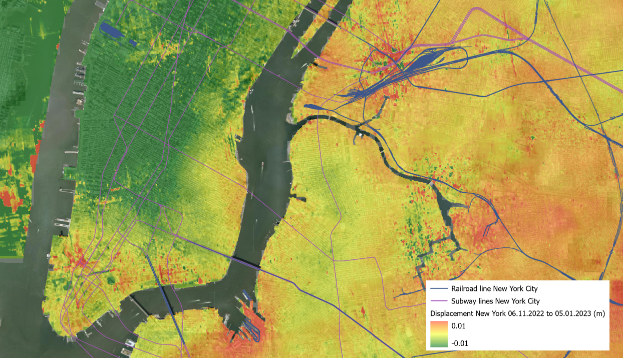
New York InSAR
Monitoring Ground Movement Using Radar and Interferometry Images: A Case Study of New York 2023
Land subsidence in New York
Introduction
Geospatial technologies are changing our understanding of Earth and land surface movements. Among the most advanced tools are radar images and their application through interferometry; techniques that allow the detection and quantification of Earth ground movement. These technologies have become crucial for understanding land subsidence and elevation, providing valuable information for risk management, urban planning, and environmental management.
Radar images enable the acquisition of highly detailed data about the Earth’s topography by emitting microwave pulses from satellites and measuring the reflected signal. Interferometry, uses the interference between waves to detect millimetre-scale changes in the height of the Earth’s surface over time. Combining these techniques, scientists have succeeded in identifying and quantifying ground movements of the land with good precision.
Case Study: New York 2023
Síor has completed a New York 2023 InSAR review. The results unveiled subsidence patterns, particularly in urbanised and coastline area; important for urban planning and risk profiling.
Research shows that land subsidence can be closely linked to human activities, i.e., groundwater abstraction and building loading, amplified by rising sea levels.
In conclusion, the use of radar images and interferometry has allowed a deeper understanding of vertical land movement. In New York, the identification of areas with greater subsidence underscores the need for adaptation and mitigation strategies in vulnerable urban areas. This technological approach not only provides a detailed insight into land dynamics, but also contributes to informed decision-making, ensuring the sustainability and resilience of our cities in the face of environmental challenges.
See our Hub for more information.

Comments (0)